
What are Lean Tools? Why should you Utilize them?
13th Jan, 2026
Lean tools are the medium through which Lean Manufacturing is carried out, with the primary aim to create value for customers by reducing non-value-added activities, thereby reducing production time and operating cost. These lean tools in manufacturing act as practical lean operations tools that help organizations stabilise processes, eliminate waste, and improve overall efficiency.
Origin of Lean Manufacturing
“The Toyota Way” is Toyota’s operating model developed in the 1930s, which laid the foundation for Lean Manufacturing and Lean Production. The objective was to optimise production and supply-chain practices while achieving operational excellence. Lean manufacturing techniques focus on using resources strictly for value creation and eliminating all other forms of waste.
The term Lean was coined in 1988 by John Krafcik and later defined in 1996 by James Womack and Daniel Jones. Lean manufacturing is built on five core principles:
- Precisely specify value from the customer’s perspective.
- Identify value-adding and non-value-adding activities.
- Ensure smooth flow of value without interruptions.
- Allow customers to pull value from the producer.
- Pursue perfection through continuous improvement.
These principles form the foundation of all lean tools and techniques used in manufacturing.
What is a Lean Organization?
A lean organization clearly understands customer value and consistently works towards delivering it through structured processes with minimal waste. Such organizations adopt lean production tools and lean manufacturing tools to achieve stable operations, predictable output, and sustained improvement. Lean tools implementation enables organizations to standardise work, reduce variation, and drive long-term performance.
What Is Waste in Lean Manufacturing?
Waste is any activity, cost, or effort that does not add value from the customer’s perspective. Since waste elimination is central to lean manufacturing, waste is categorised using the 3Ms of Lean:
- Muri (Overburden): Excessive stress on people or equipment caused by poor planning or unrealistic workloads
- Mura (Unevenness): Variability in production schedules, quality, or volume that creates instability
- Muda (Waste): Non-value-adding activities identified after processes are in place
These categories help organizations apply lean tools for waste reduction in a structured manner.
.
Unlock Process Efficiency and Waste Reduction Using Lean Tools
What Are Lean Tools?
Lean manufacturing tools assist in the systematic identification and elimination of waste while enabling effective lean manufacturing techniques. These tools support a disciplined approach to lean tools for process improvement, ensuring consistent performance and measurable results.
With proper training and lean tools implementation, organizations can:
- Eliminate waste
- Improve quality
- Reduce lead time
- Lower production and operational costs
Below is a practical lean manufacturing tools list widely used across manufacturing industries.
Lean Manufacturing Tools List:
Lean manufacturing tools assist in the identification and steady elimination of specific waste and helps in implementing Lean Manufacturing Practice efficiently and effectively. The tools enable organizations to ensure a relentless pursuit of reducing waste and achieve consistent improvement. With training and implementation, you can eliminate waste and improve quality along with drastically reducing production time and cost.
Here are the lean tools that will help you carry out your lean manufacturing practice efficiently and effectively.
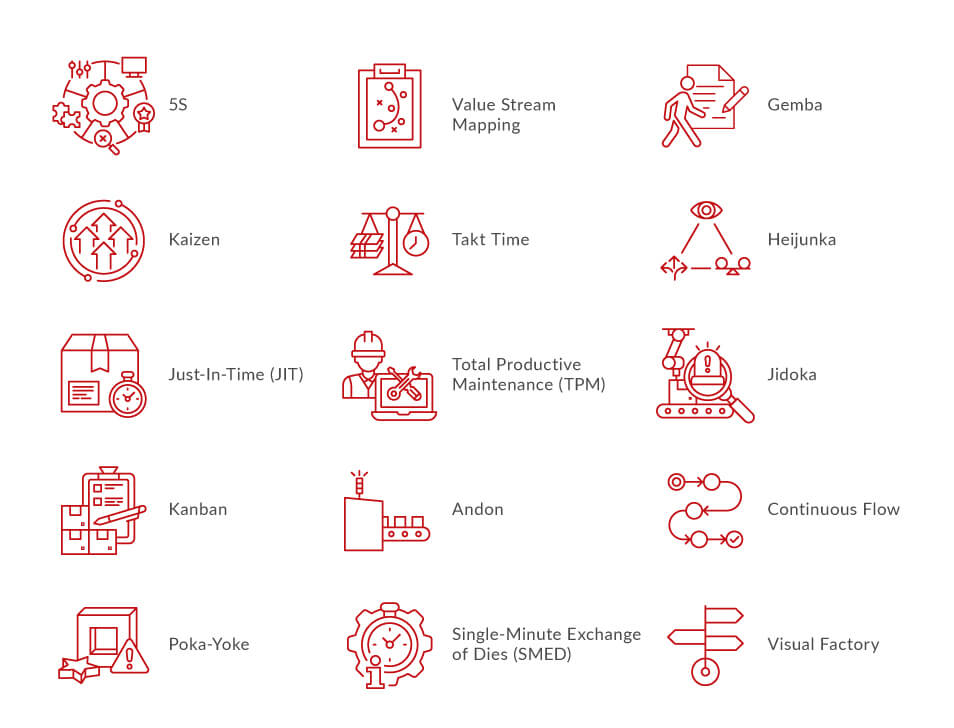
5S
Eliminates waste that results from a poorly organised work area, such as time wasted searching for tools or materials.
- Sort: Eliminate items that are not required
- Set in Order: Organise remaining items for easy access
- Shine: Clean and inspect the work area
- Standardise: Define standards for organization and cleanliness
- Sustain: Maintain and regularly apply standards
Kaizen
Kaizen stands for continuous improvement. It focuses on a strategy where employees work together proactively to achieve regular, incremental improvements in manufacturing processes.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
Just-In-Time pulls parts through production based on actual customer demand instead of pushing production based on forecasts, helping reduce inventory and overproduction.
Kanban
Kanban is a pull-based system used to regulate the flow of goods within the factory and between suppliers and customers. It helps eliminate waste caused by excess inventory and overproduction.
- Poka-Yoke
- Poka-Yoke refers to error-proofing techniques designed to prevent defects or detect them immediately. Since detecting and correcting defects becomes more expensive at later stages, this tool helps ensure quality at the source.
- Value Stream Mapping
- Value Stream Mapping visually maps the flow of production by detailing every step in the process. It shows the movement of goods from supplier to customer and highlights opportunities for improvement.
- Takt Time
- Takt Time defines the time required to produce a product to meet customer demand. It aligns the pace of production with demand.
Formula: Planned Production Time ÷ Customer Demand
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- TPM is a holistic methodology aimed at maintaining proactive and uninterrupted production. It promotes shared responsibility for equipment maintenance and increases operator involvement to maximise equipment availability.
- Andon
- Andon is a visual status-display system used on the shop floor to alert operators and managers of production issues in real time, enabling immediate corrective action.
Continuous Flow
Continuous Flow is a production method where work-in-process moves smoothly through operations with minimal or no buffers between steps.
Gemba
Gemba means “the actual place.” It encourages managers and leaders to spend time on the shop floor to understand real manufacturing issues through direct observation and employee interaction.
Heijunka
Heijunka refers to production leveling. It reduces unevenness in workloads and minimises the risk of overburdening people or equipment.
Jidoka
Jidoka, also known as autonomation, focuses on product quality by stopping production when abnormalities occur, preventing defective products from reaching customers.
Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)
SMED reduces setup or changeover time to less than 10 minutes using techniques such as:
- Converting internal setup steps to external.
- Simplifying internal setup (e.g., replacing bolts with levers).
- Eliminating non-essential operations.
- Creating standardised work instructions.
Visual Factory
Visual indicators, displays and controls are used throughout manufacturing plants to improve communication of information. It consists of a set of charts, direction signage, information representation that enables quick dissemination of data.
Why You Need Lean Tools in Manufacturing?
Lean tools help manufacturing organizations reduce waste, improve productivity, and achieve operational excellence by eliminating non-value-added activities and stabilising processes. The benefits of lean tools in manufacturing include lower production costs, improved quality, faster lead times, and a structured approach to continuous improvement across operations.
Waste Reduction in Manufacturing Operations:
Lean tools in manufacturing systematically identify and eliminate non-value-added activities such as excess inventory, waiting time, motion, and defects. Lean tools for waste reduction like Value Stream Mapping and Kanban expose inefficiencies within material and information flow. This enables organizations to reduce waste while maintaining stable and predictable production.
Improved Productivity and Process Efficiency:
Lean manufacturing techniques stabilise workflows and reduce process variation, leading to consistent output and higher productivity. Lean tools for process improvement such as Takt Time and Continuous Flow align production with customer demand and eliminate bottlenecks. This demonstrates how lean tools improve productivity without increasing resources.
Lower Production and Operating Costs:
Lean tools reduce rework, inventory holding, changeover losses, and unnecessary handling, directly lowering production and operating costs. Tools like SMED and Just-In-Time reduce non-productive time and excess stock levels. This clearly explains why companies should use lean tools to improve cost performance.
Improved Quality and Defect Prevention:
Lean tools focus on building quality into the process rather than detecting defects after production. Poka-Yoke and Jidoka prevent errors from progressing downstream by stopping processes when abnormalities occur. This results in reduced scrap, rework, and customer complaints.
Continuous Improvement Through Employee Involvement:
Lean tools for continuous improvement promote structured problem-solving at all organizational levels. Practices such as Kaizen and Gemba engage shop-floor teams in identifying root causes and implementing corrective actions. This creates sustained improvement rather than isolated efficiency projects.
Operational Excellence and Process Stability:
Lean tools support operational excellence by standardising work, balancing workloads, and improving equipment reliability. Visual Factory, Heijunka, and Total Productive Maintenance improve visibility, production leveling, and asset performance. These controls prevent firefighting and support long-term operational stability.
Scalable Across Manufacturing Organization Sizes:
Lean tools are adaptable and effective for organizations of different scales. Lean tools for small and medium enterprises typically start with 5S, Visual Management, and Kaizen, while lean tools for large manufacturing organizations expand into Kanban systems, TPM, and Jidoka. This flexibility clarifies who should use lean manufacturing tools across industries.
How 4C Helps Organizations Implement Lean?
At 4C Consulting, we provide end-to-end Lean Six Sigma implementation support tailored to industry-specific operational needs, helping organizations achieve measurable and sustainable performance improvements. Our experienced consultants combine expert-led training, hands-on project execution, and effective deployment of Lean Six Sigma tools to drive real results on the shop floor. With experience supporting over 45 clients, delivering 1,300+ training hours, and enabling 60+ professional certifications, we focus on practical application rather than theoretical adoption. By integrating Lean Six Sigma with Total Quality Management (TQM) principles, 4C helps businesses improve process efficiency, reduce waste, control costs, and enhance customer satisfaction in a structured and cost-effective manner. Connect us now.
📥 You can download Lean Manufacturing Tools PDF


