Frequently Asked Questions ISO 45001
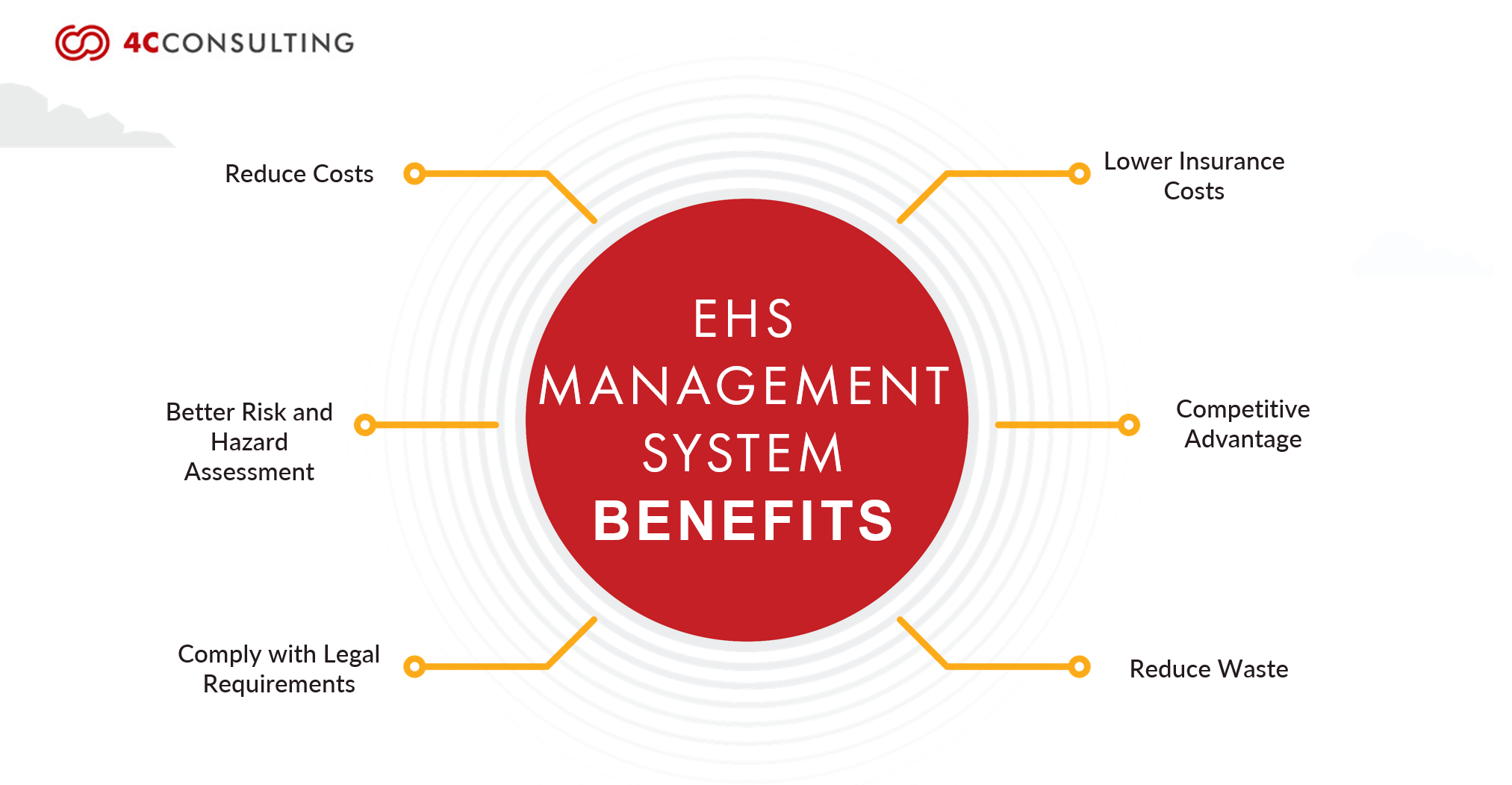
The ISO 45001 standard brings various benefits to organizations by focusing on occupational health and safety. Here are some key advantages:
Safety: ISO 45001 enhances workplace safety, reducing accidents and illnesses.
Legal Compliance: Ensures adherence to health and safety regulations, minimizing legal risks.
Cost Savings: Proactive risk management leads to reduced expenses and insurance premiums.
Global Recognition: Opens doors to international markets by demonstrating high safety standards.
Efficiency: Streamlines processes, improving overall operational efficiency.
Reputation: Boosts organizational reputation by prioritizing employee well-being.
Employee Engagement: Fosters employee involvement, creating a sense of responsibility.
Continuous Improvement: Promotes a culture of ongoing refinement in health and safety practices.
Supply Chain Confidence: Reassures suppliers and partners of a commitment to safety.
An ISO 45001 audit, whether internal or external, involves a thorough examination of an organization's health and safety management system. It aims to ensure compliance with ISO 45001 standards, identify areas for improvement, and verify the effectiveness of the system. Results may include non-conformances that require corrective actions and insights for continuous enhancement of occupational health and safety practices. Internal audits are conducted by the organization itself, while external audits are performed by independent certification bodies.
Organizations opt for ISO 45001 certification for several compelling reasons:
Safer Workplace: Focus on creating a secure work environment.
Legal Compliance: Alignment with health and safety regulations.
Global Recognition: Internationally accepted certification.
Reputation Boost: Enhanced trust with stakeholders.
Cost Savings: Reduction in accident-related expenses.
Employee Morale: Increased satisfaction and positive culture.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes for better productivity.
Competitive Edge: Signals commitment to safety and quality.
Risk Management: Proactive identification and management of risks.
Continuous Improvement: Encourages an ongoing commitment to getting better.